AUTHORHS & EDITORS
DNA (deoxyribonucleotid acid) is a double-stranded poly- mer of four nucleotides: adenine, cytosine, thymine and guanine (Figure 1). The two strands interact together by hydrogen bonds between pairs of nucleotides. The information needed for protein biosyntheses is determined by the genetic code and is inherent through replication microscope slides or chips in arrays by forming chemical bonds. The purpose of these “DNA arrays” is to identify if tagged fluorescently nucleic acids Abstract. This chapter provides an overview of DNA microarrays. Microarrays are a technology in which ’s of nucleic acids are bound to a surface and are used to measure the relative concentration of nucleic acid sequences in a mixture via hybridization and subsequent detection of the hybridization blogger.com: Roger Bumgarner

JOURNAL CALL FOR PAPER
So DNA microarray is most powerful technology which can fluorescently labeled target sequences that bind to a probe sequence generate a signal that depends on the strength provide a high throughput and detailed view of the entire genome and transcriptome which allows scientists to of the hybridization determined by the number of paired understand the molecular mechanisms Estimated Reading Time: 11 mins DNA microarray and next-generation DNA sequencing technologies are important tools for high-throughput genome research, in revealing both the structural and functional characteristics of genomes. In the past decade the DNA microarray technologies have been widely applied in the studies of functional genomics, systems biology and pharmacogenomics Microarray can be a boon to researchers as it provides a platform for simultaneous testing of a large set of genetic samples. It helps especially in the identification of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and mutations, classification of tumors, identification of target genes of tumor suppressors, identification of cancer biomarkers, identification of genes associated with

Publication types
· Microarrays allow DNA and RNA hybridization analysis in a parallel fashion on miniaturized platforms. The number of test sites in microarrays varies from a few hundred to several hundreds of Author: Sam Kassegne Microarray can be a boon to researchers as it provides a platform for simultaneous testing of a large set of genetic samples. It helps especially in the identification of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and mutations, classification of tumors, identification of target genes of tumor suppressors, identification of cancer biomarkers, identification of genes associated with So DNA microarray is most powerful technology which can fluorescently labeled target sequences that bind to a probe sequence generate a signal that depends on the strength provide a high throughput and detailed view of the entire genome and transcriptome which allows scientists to of the hybridization determined by the number of paired understand the molecular mechanisms Estimated Reading Time: 11 mins

Microarray can be a boon to researchers as it provides a platform for simultaneous testing of a large set of genetic samples. It helps especially in the identification of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and mutations, classification of tumors, identification of target genes of tumor suppressors, identification of cancer biomarkers, identification of genes associated with How to publish research paper Research Paper Topics What is DOI? Benefits of DOI Journal Indexing Open Access Journal: About IJSER IJSER is an online international open access peer review scholarly journal published monthly. Indexing is an important part of journal, indexed content at the article level, also provide DOI for the articles Abstract. This chapter provides an overview of DNA microarrays. Microarrays are a technology in which ’s of nucleic acids are bound to a surface and are used to measure the relative concentration of nucleic acid sequences in a mixture via hybridization and subsequent detection of the hybridization blogger.com: Roger Bumgarner
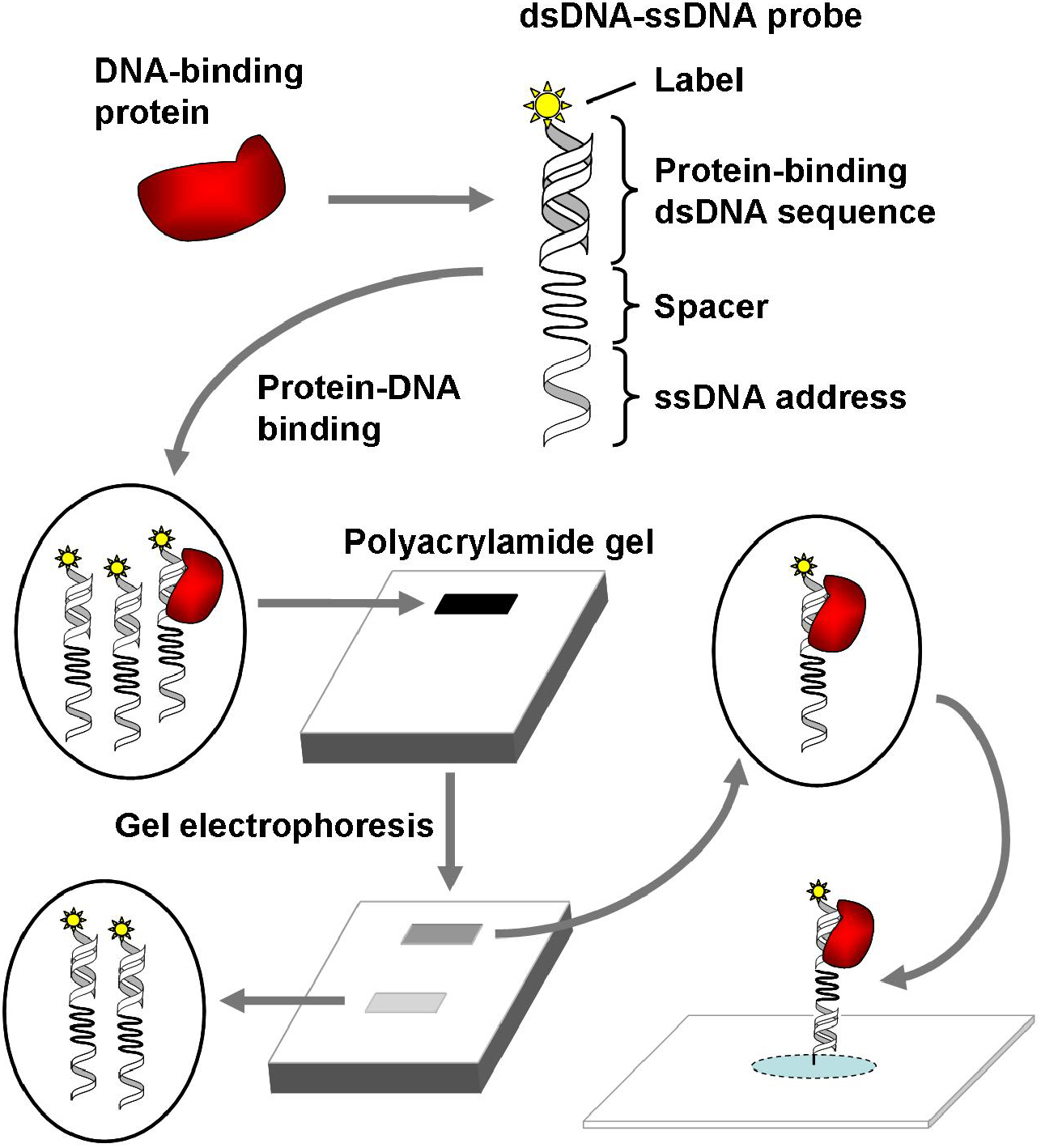
microscope slides or chips in arrays by forming chemical bonds. The purpose of these “DNA arrays” is to identify if tagged fluorescently nucleic acids DNA microarray and next-generation DNA sequencing technologies are important tools for high-throughput genome research, in revealing both the structural and functional characteristics of genomes. In the past decade the DNA microarray technologies have been widely applied in the studies of functional genomics, systems biology and pharmacogenomics · Despite continuous improvements and modification to the technique, DNA microarrays are still no more than a glass microscope slide studded with individual immobile nucleotide fragments (1, 2). The fundamentals of DNA microarrays are set on complementary base-pairing (3), and because the exact sequence and position of every segment on the slide
No comments:
Post a Comment